Auto lending is currently 40% higher than the last peak in 2003.
Auto leases are growing at a 20% annual rate.
The average car loan term is now 66 months, the highest in U.S. history.
The average amount financed is at an all-time high of $27,612.
The average monthly payment reached a new all-time high of $474.
The percentage of subprime deadbeats getting car loans has soared to 34% of all loans.
Lenders are doling out loans that are 25% higher than the value of the autos they are “selling”. A new car depreciates 10% the second you drive it off the lot.
Real household income is 7% lower than it was in 2007, while gas, utilities, food, health insurance, and taxes are significantly higher. The entire consumer spending “recovery” has been nothing but another Federal Reserve/US Treasury engineered debt bubble of auto and student loans. The piper will be paid. The bubble will burst. The losses will be epic. Who coulda knowed? I bet you can’t wait to bail out Wall Street and Obama again. You’ll do it for the children.
Via David Stockman’s Contra Corner
By Editor, Fabius Maximus, a multi-author website with a focus on geopolitics. Reposted from Wolf Street
http://wolfstreet.com/2014/08/07/auto-loans-once-a-boon-for-america-now-malignant/
One of the many oddities of this cycle is that many things that were good during the post-WW2 era have become bad in the era now starting (unrecognizably so, as we remain unaware of our changed circumstances). Like debt. Such as auto loans. Our use of debt gives clues to our future..
Consumer debt in the old world, and the new
During the post-WW2 era increasing debt supercharged economic growth for the young and rapidly-growing West. But after 60 years of this our societies now carry massive debt loads, both public and private — while the numbers of elderly grow (who experience a crash of income upon retirement, plus rising costs to society for their pensions and health care). Carrying our current load might prove difficult; adding to it now is madness.
Plus, there are other factors in play. Fifty years of growing inequality, for still poorly-understood reasons, have hollowed out the middle class — diminishing their ability to carry their existing debt, making them dependent on borrowing to maintain their lifestyle.
Some take another step beyond borrowing. Borrowing to buy cars and homes results in slowly accumulating equity, one of the most common ways middle class households save. Increasingly Americans abandon buying with debt for renting. Rent homes instead of owning. Renting cars (leasing) instead of owning.
Automobile sales point to our new world
Accelerating borrowing was a natural leading indicator of economic recoveries during the post-WW2 era. So economists see the waves of desperate borrowing by consumers since 2000 as a good thing. Hence their excitement about the subprime lending boom that drove the housing bubble. Such as today’s subprime borrowing to buy cars.
The extreme case of this blindness to our changed conditions is glee about the shift to renting cars (aka leasing). It shows vibrant demand for cars! As we see in this excerpt from a report by BofA-Merrill global economist Ethan Harris, 6 August 2014, showing that after mid-2012 leasing grew faster than total spending on vehicles (2012 saw many such transition points for the US economy).
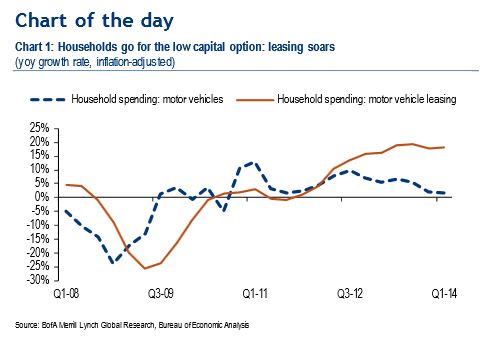
Households go for the low capital option: leasing soars:
Household outlays on leasing are booming at a 20% yoy pace — a clear sign that demand for vehicles is alive and kicking. With average lease payments lower than typical monthly ownership costs and with a down-payment not typically required to enter into a lease, the surge in vehicle leasing is likely a sign that financial restraints are still holding back some would-be buyers. Thus, as the economy improves, bottled-up household demand for vehicles could translate to higher sales.
Yes, in our society demand is “alive and kicking” by subprime households for cars bought with low-rate loans on easy terms — or even just renting (aka leasing). But does it point to an economic recovery — or exhaustion?.
The terms are very easy
Turning back to people at least attempting to buy, there are four dimensions to consumer loans: the creditworthiness of the borrower, the interest rate of the loan, the length of the loan, and the collateral (the loan to value ratio). A report by Experian Automotive, 2 June 2014, describes the first three.
… average automotive loan term reached an all-time high of 66 months … loans with terms 73-84 months grew to 25% of all loans originated during the quarter. …
The average amount financed for a new vehicle loan also reached an all-time high of $27,612 in Q1 2014, up $964 from the previous year. In addition, the average monthly payment for a new vehicle loan reached its highest point on record at $474 in Q1 2014, up from $459 in Q1 2013.
… Market share for nonprime, subprime and deep subprime new vehicle loans in Q1 2014 rose to 34%.
Six- and seven-year-long auto loans! At what point will the borrower have equity in their cars? Especially since these are probably the subprime borrowers that make up 1/3 of auto lending.
The fourth factor is equally ugly. Lenders are lending more than the value of the collateral (i.e., including closing costs and rolling over the deficit of the buyers’ trade-in). These are averages; half of loans have even higher LTVs. From Semiannual Risk Perspective, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, Spring 2014:
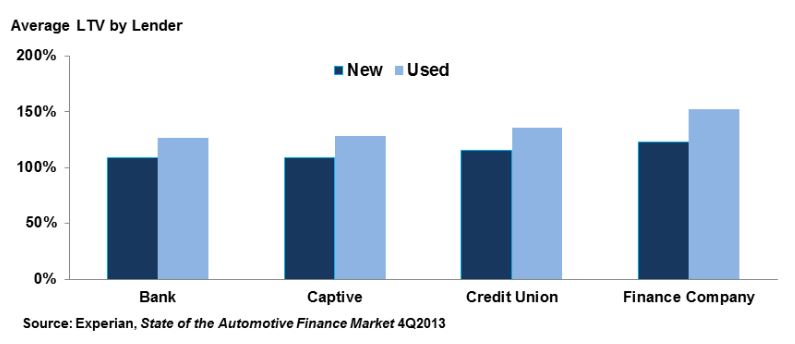
Why are these numbers important?
The changing nature of auto sales tell us much about ourselves. They show how economists do not see the new era beginning. They imply slower growth in the future, as a household’s longer loans with smaller down payments push out their ability to buy their next car. They tell us something about the recovery.
Auto sales have been a major driver of the recovery. Most economists expect auto sales to continue growing, helping power the long-awaited acceleration from slow ~2% growth to 3% or beyond. So the sustainability of auto sales — and the borrowing and leasing that fuels them — matter.
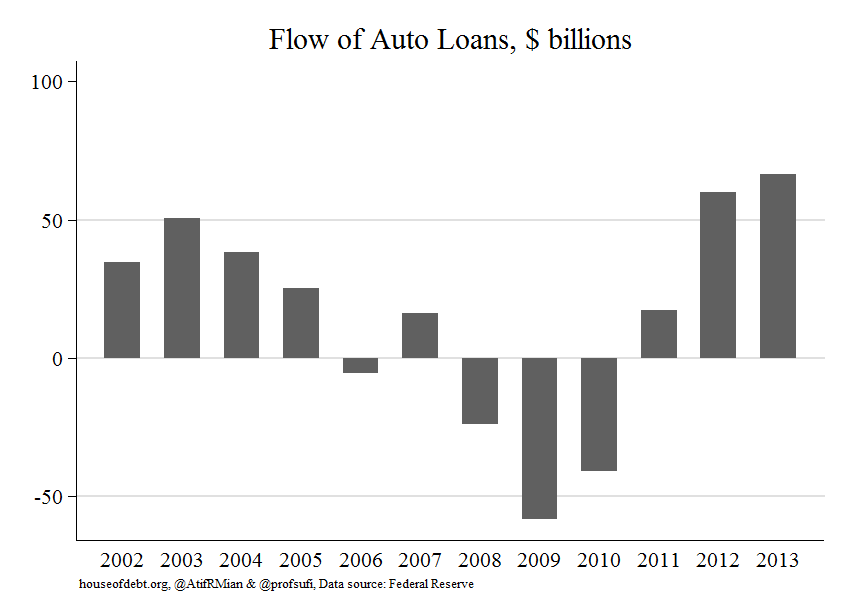
Atif Mian and Amir Sufi show the importance of auto loans to auto sales, and of auto sales to consumer sales. These are from their post “Another Debt-Fueled Spending Spree?“, 31 March 2014. First, lending is rapid:
Second, since the crash, auto sales have grown much faster than overall consumer spending.
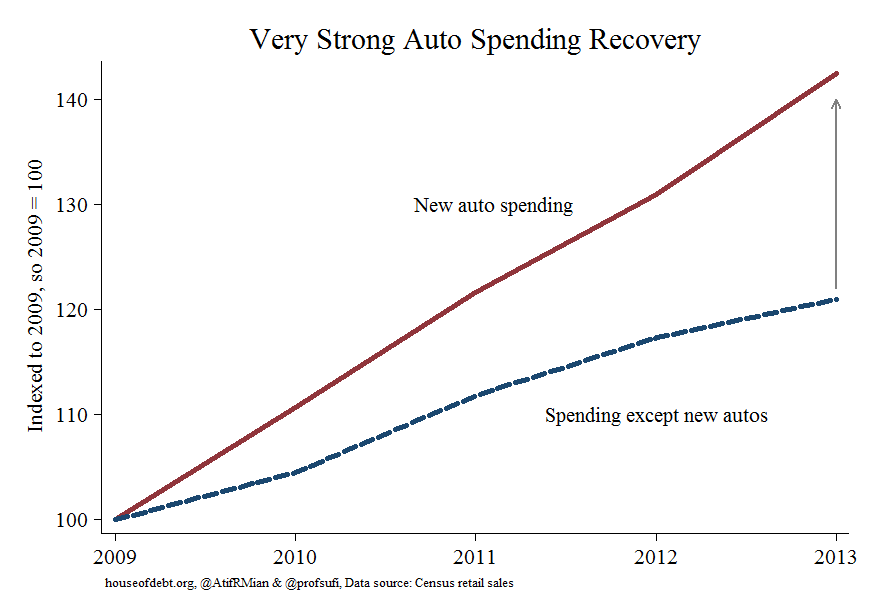
Auto sales have been one of the few drivers of this recovery. They have been pushed up by easy credit, longer terms, lower credit quality, and sky-high loan-to-value ratios. But these loans lock the buyer out of the market for years to come. Charge-off for lenders will rise, and in response lenders will re-tighten their underwriting standards. And outstanding auto loans, once useful in the prior era, will become malignant. By Editor, Fabius Maximus.
The US economy has repeatedly failed to resume normal growth after the crash. But potentially worse is the decline in long-term growth estimates. Read…. Has America’s Economy Entered the “Coffin Corner”?













